Dear students,
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!- You are kindly asked to fitch the Handout from the Alanwar Copy center.
- I will share here the theoretical part of the expository and argumentative essays (The practical part in the handout)
- Your comments, remarks, and questions should be shared in the comment section
1. Expository Writing
1.1. What is Expository Writing?
Expository writing is writing to explain. Expository writing seeks to inform, explain, clarify, define or instruct.

How is Expository Writing different from other types of writing?
•Expository writing does not tell a story.
•Expository writing does not persuade a reader but only gives facts and reasons.
•Expository writing is not a summary of the book.
•Expository writing is not a book review or a book report.
•Expository writing is not ONLY your opinion. You must base your ideas on evidence from the text.
Characteristics of Expository Writing
- Focus on main topic
- Logical supporting facts
- Details, explanations, and examples
- Strong organization
- Clarity
- Unity and coherence
- Logical order
- Smooth transitions
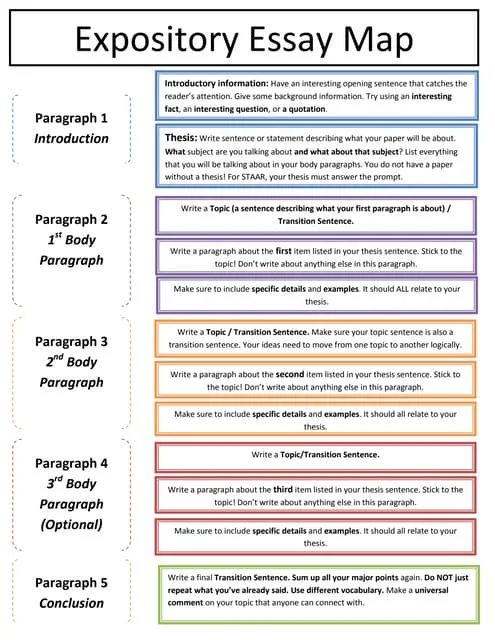
The Expository Essay Format