The simple present tense is one of the most fundamental aspects of English grammar. Whether you’re just starting out or need a refresher, mastering the simple present tense is essential for everyday communication. This article will break down the simple present tense, explain its uses, and provide engaging exercises to reinforce your learning.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!1. What is the Simple Present Tense?
The simple present tense refers to actions that occur regularly or facts that are always true. Unlike other tenses that focus on time or duration, the simple present primarily focuses on timeless events, habitual actions, and universal truths.
Example:
- “She reads books every evening.”
- “The Earth orbits the Sun.”
2. Forms of the Simple Present Tense
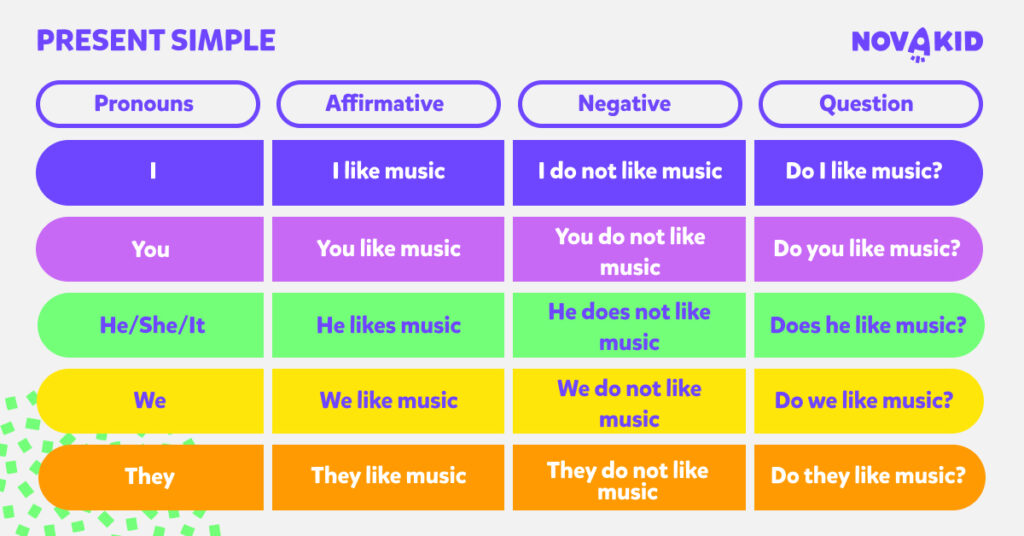
The simple present has two basic forms: affirmative and negative. Additionally, questions in the simple present use the auxiliary verbs “do” or “does.”
- Affirmative: I play football.
- Negative: She does not (doesn’t) like pizza.
- Question: Do they live nearby?
3. Uses of the Simple Present Tense
a. Repeated Actions or Habits
The simple present is often used to talk about habits or routines—actions that happen repeatedly.
- “She drinks coffee every morning.”
- “They watch TV every weekend.”
b. General Facts and Truths
Statements that express general knowledge or facts also use the simple present tense.
- “Water boils at 100°C.”
- “The sky appears blue on a clear day.”
c. Scheduled Events in the Near Future
The simple present is sometimes used to refer to scheduled events, especially with transportation or official programs.
- “The train leaves at 6 PM.”
- “The meeting starts at noon.”
d. Instructions and Directions
When giving directions or instructions, the simple present tense is commonly used.
- “Turn left at the next street.”
- “First, you mix the ingredients.”
4. Forming Simple Present Sentences
a. Positive Sentences
In positive sentences, the simple present follows the formula: Subject + base verb (+ s/es for third-person singular)
- “I play the guitar.”
- “He plays the guitar.”
b. Negative Sentences
For negative sentences, the formula is: Subject + do/does not + base verb
- “She does not (doesn’t) like sports.”
- “We do not (don’t) own a car.”
c. Questions in the Simple Present Tense
To form questions, the structure is: Do/Does + subject + base verb
- “Do you like ice cream?”
- “Does she work here?”
5. Conjugation of Verbs in Simple Present Tense
The verb conjugation in the simple present is straightforward, but there’s a key difference between first-person, second-person, and third-person singular.
- I/You/We/They: base verb (e.g., “play”)
- He/She/It: base verb + s/es (e.g., “plays”)
Examples:
- “I run every day.”
- “She runs every day.”
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forgetting the -s for third-person singular:
- Incorrect: “She go to school.”
- Correct: “She goes to school.”
- Using “do” with third-person singular without “does”:
- Incorrect: “He do not like pizza.”
- Correct: “He does not like pizza.”
7. Irregular Verbs in the Simple Present Tense
While most verbs in the simple present tense simply add “s” or “es” for third-person singular, some irregular verbs don’t follow this rule. The most common irregular verb is “to be.”
- I am, You are, He/She/It is, We/They are
8. How to Recognize When to Use Simple Present Tense
Look for time expressions like “always,” “every day,” “never,” and “usually.” These signal the need for the simple present tense.
Example:
- “I usually wake up early.”
- “He always tells the truth.”
9. The Importance of the Subject-Verb Agreement
In English, ensuring that the subject and verb agree in number is critical in the simple present tense. This is particularly important with singular and plural forms.
Example:
- “She writes emails.” (Singular)
- “They write emails.” (Plural)
10. Short Answers in the Simple Present Tense
In conversation, it’s common to give short answers rather than repeating the entire sentence.
Example:
- Question: “Do you speak English?”
- Answer: “Yes, I do.” or “No, I don’t.”
11. Adverbs of Frequency and the Simple Present Tense
Adverbs like “always,” “never,” and “often” are used to show how frequently something happens in the simple present tense.
- “She always forgets her keys.”
- “I never eat fast food.”
12. Exercises of Simple Present Tense
– Exercise 1 of Simple Present Tense
– Exercise 2 of Simple Present Tense
– Exercise 3 of Simple Present Tense
– Exercise 4 of Simple Present Tense
Read Also: 10 Foreign emotion words with no English equivalent
Tautology: Understanding the Art of Redundancy in Language
When do I use the simple present tense?
You use the simple present to describe habitual actions, general truths, and scheduled events.
What are the most common adverbs of frequency used with the simple present tense?
Adverbs like “always,” “often,” “usually,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never” are commonly used.
How do I form a question in the simple present tense?
To form a question, use “do” or “does” before the subject: “Do you play tennis?” or “Does she live nearby?”
What is the difference between “do” and “does”?
Use “do” with I/You/We/They and “does” with He/She/It.
Can I use the simple present to talk about the future?
Yes, but only when discussing scheduled events (e.g., “The plane leaves at 6 PM tomorrow”).
How do I know if a verb is irregular in the simple present?
Irregular verbs like “to be” do not follow the regular pattern of adding “s” or “es” for third-person singular forms.







