In a nutshell, Lyons (1981) defines linguistics as the scientific study of language. Many people assume that linguistics is merely attached to academia. Linguistics, however, covers different areas in our life. It is concerned with the systematic study of human language in all its aspects and manifestations:
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!1. Linguistics: Definition
- Language structure;
- Language use (communication);
- Language and history;
- Language and society and many other areas;
Linguistics is a very wide-ranging field of study that attempts to understand one of the most intricate traits of humans- language. Thus, Linguists (experts in linguistics) are striving to answer some of these questions:
- · What makes human language so special and different from other animal communication systems?
- Why is language so important to humans?
- What are the properties of language?
- How does a child acquire a mother tongue and learn a foreign language?
- How do culture and society influence language?
These are just a few questions among many others that linguistics tries to answer.
Read also: Will English be the major Lingua Franca?
2. The aim of linguistics
 |
| Source: 123RF |
The main goals of linguistics are to:
- to study particular languages and look for the shared properties of human languages; that is to say, to look for common points and shared features between languages;
- to bring our unconscious knowledge of language to the level of consciousness;
- to study how the different units of language are combined and how they operate in the human brain.
3. What makes linguistics scientific?
A. Linguistics is objective
All languages are equal and there is no pure, primitive, beautiful, sophisticated, rich, or prestigious language. Unfortunately, laypeople keep labeling their languages as advanced and others as barbaric.
B. Linguistics is an empirical discipline
Linguists are seen as people who strive to learn many languages, master grammar, and have rich vocabulary. In fact, their mission goes beyond that. They are researchers who systematically examine the obtained data (e.g. speech production) about any language following scientific measurements- observations, testing hypotheses, and finally developing theories. In other words, that is to say, linguistics is based on experiments rather than intuitions or speculations.
4. Branches and Subfields of linguistics
Due to the fact that language is one the most important traits that humans possess, linguistics intertwines with many other fields of study. As a result, a lot of branches emerge to cover many areas ranging from sociolinguistics, pragmatics, neurolinguistics, psycholinguistics, applied linguistics, computational linguistics, and finally theoretical linguistics.
Linguistics is very broad, with many different fields. When you have the chance to delve into scrutinizing linguistics, you will come across many of these areas and aspects of the human language including:
A. Phonetics: the study and classification of speech sounds. It Ideals with acoustics phonetics, auditory phonetics, and articulatory phonetics.
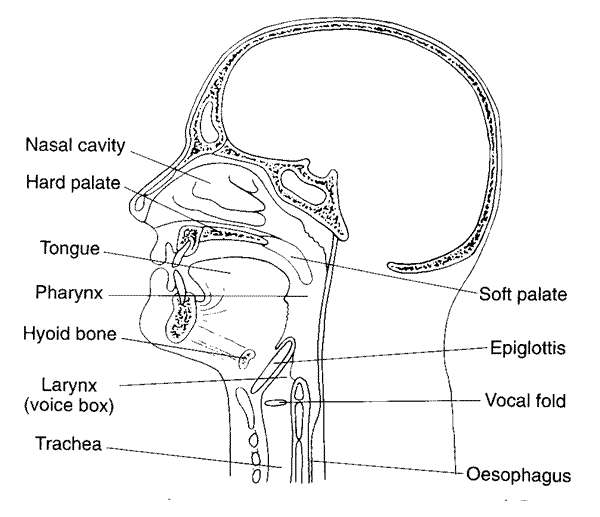 |
| Source: Linguistics 001 |
B. Phonology: the study of speech and patterning of sounds in a specific language or between different languages.
C. Morphology: the study of the structure(s) and the formation of words
D. Syntax: the study of the structure and the formation of sentences.
 |
| Source:Ua Stundent |
E. Semantics: the study of language meaning.
F. Pragmatics: deals with the study of language in context and language use
If you think these tips are useful, please “SHARE AND CARE”






